LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screens have become an integral part of our daily lives, being widely used in devices such as televisions, computer monitors, and smartphones. While LCD technology offers several advantages, one of its inherent limitations lies in its restricted color gamut, which poses challenges in accurately reproducing certain colors. This article delves into the factors contributing to the limited color gamut of LCD displays and explores potential solutions to improve color accuracy.
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screens have become an integral part of our daily lives, being widely used in devices such as televisions, computer monitors, and smartphones. While LCD technology offers several advantages, one of its inherent limitations lies in its restricted color gamut, which poses challenges in accurately reproducing certain colors. This article delves into the factors contributing to the limited color gamut of LCD displays and explores potential solutions to improve color accuracy.
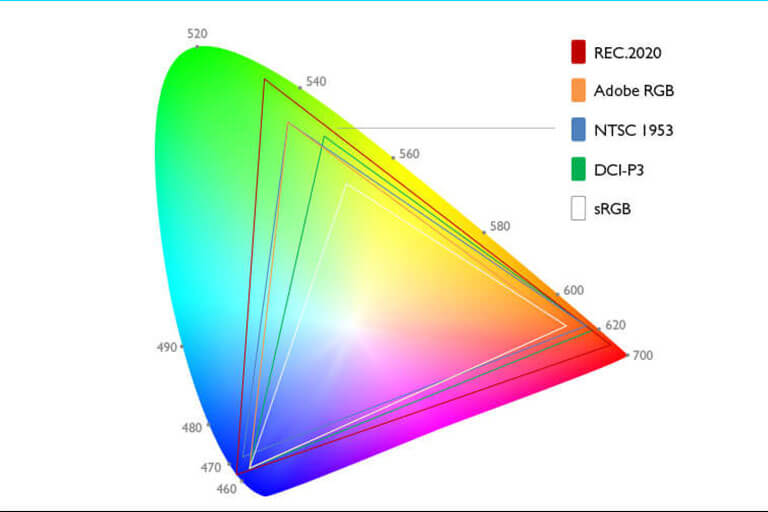
Color Gamut and Color Reproduction: Color gamut refers to the range of colors that a display can reproduce. LCD panels rely on a backlight source and a color filter array to display colors. However, due to the properties of these components, LCD displays typically exhibit a smaller color gamut compared to other display technologies, such as OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays.
Challenges in Color Accuracy: The limited color gamut of LCD displays can result in challenges when accurately reproducing certain colors, especially those outside the display’s gamut range. This can lead to color inaccuracies, such as oversaturated or undersaturated colors, and a loss of detail in subtle color gradients.
Impact on Visual Content: Inaccurate color reproduction can have a significant impact on various applications, including image editing, graphic design, and professional photography. Colors that fall outside the display’s gamut may appear different or distorted, making it difficult for users to achieve desired color accuracy and consistency across different devices.
Solutions for Improved Color Accuracy:
- a) Display Calibration: Calibration tools and software can help adjust the color settings of LCD displays to achieve a more accurate representation of colors. This process involves measuring color accuracy, adjusting color profiles, and fine-tuning display parameters to match desired color standards.
- b) Enhanced Color Management: Advanced color management techniques can be implemented to compensate for the limitations of LCD displays. These techniques involve color mapping and color space conversions to optimize color reproduction and ensure consistent color accuracy across different devices and media.
- c) Adoption of Wide Color Gamut (WCG) Technologies: LCD displays with wider color gamuts, such as those using quantum dot or mini-LED technologies, can provide a broader range of colors and improve color accuracy. These technologies expand the gamut coverage, allowing displays to reproduce more vibrant and nuanced colors.
Conclusion: While LCD displays offer numerous benefits, their limited color gamut remains a challenge in accurately representing certain colors. To address this limitation, display calibration, enhanced color management, and the adoption of wide color gamut technologies can be employed. As the demand for more precise color reproduction continues to grow, advancements in display technology will play a vital role in improving the color accuracy and enhancing the overall visual experience provided by LCD screens.